在迷宫算法总结篇中我总结了生成迷宫的四种算法,在这一篇文章里面我侧重迷宫游戏的实现以及可视化。
使用python3中的GUI绘图库tkinter实现了一个简陋版的迷宫游戏,地图截图如下图所示。
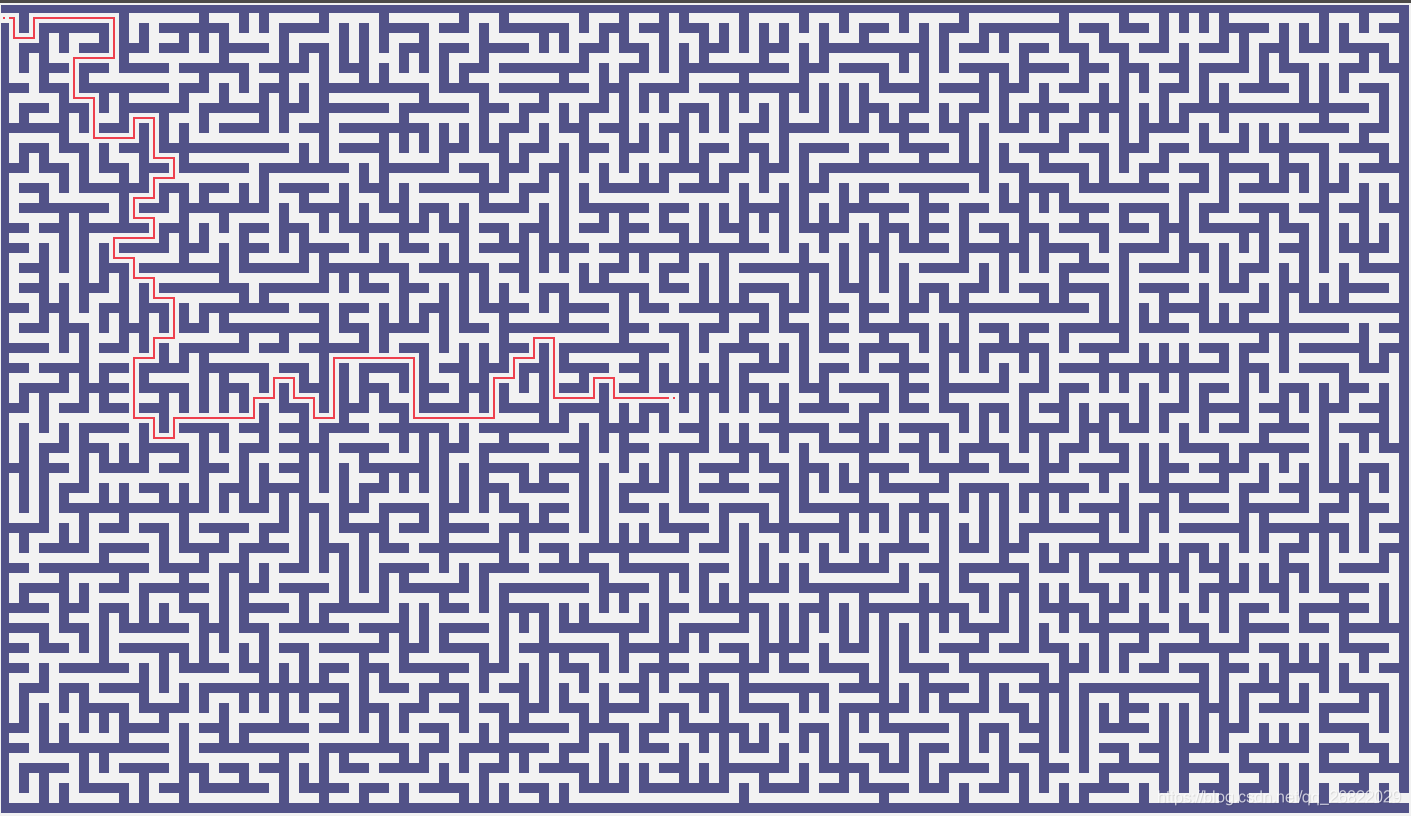

为了降低游戏的难度,在寻找路径的过程中你可以通过点击图中的空白点,生成从起点到你点击位置的路径。迷宫的难度主要由以下几个参数决定:
- 迷宫的长和宽:尺寸越大,生成的地图越难
- 迷宫生成算法:地图难度:kruskal算法 > 随机深度优先算法 > prim算法 > 递归分割算法。
目前已经开发到版本1.0.7,已经实现的功能有:
当前版本代码在Maze-game-v1.0.7.
- 游戏背景音乐
- 游戏难度递增
- 增加状态栏显示状态信息
- 作弊(查看提示)增加惩罚分数(当前作弊一次惩罚20分)
- 保存读取地图
- 菜单栏,可用于设置地图生成算法,地图尺寸等
- 增加迷雾模式
- 增加生存模式,参考Roguelike Vision Algorithms丰富可玩性
- 显示等级以及当前移动步数
- 随机生成游戏地图
- 按方向键后自动前进倒退(到分岔路停止)
- 起点到任意位置辅助路径显示(鼠标左键单击空白地方显示路线) 移动次数计数
- 到达终点后通关,按任意键进入下一关(目前没有难度设置,难度相同)
出现过的bug列表:
-
到达终点后上下左右键仍然可用且不会进入到下一关
已解决:修改进入下一关的逻辑 -
画图很慢,不知道是我代码写的垃圾还是这个python的tkinter库本身的问题[狗头]
已解决:刷新也面前调用Canvas.delete(“all”)清除之前绘制的所有内容再画新的页面即可。 -
通关后生成的地图绘制的就更慢了,按一次方向键后要等一年[狗头]
已解决:同上
最新版本截图
1 简单模式
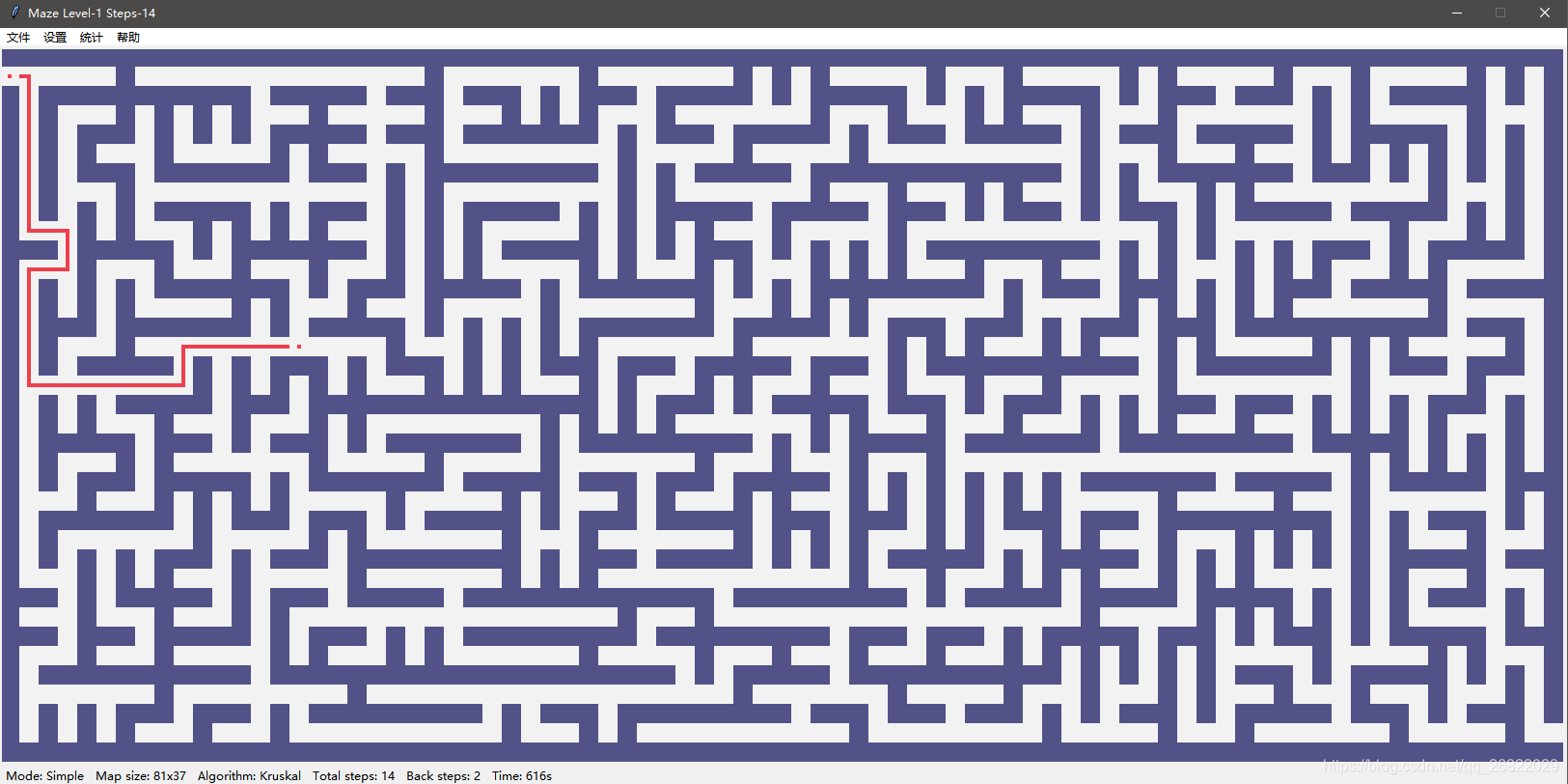

2 迷雾模式


详细的介绍以及说明后续补充。现在提供1.0.3版本源码清单如下,为了方便代码管理,后续版本代码将会直接上传到Github,目前已经更新到v1.0.7,最新版本代码Maze-game-v1.0.7.
- 迷宫类 Maze:
├ print_matrix
├ generate_matrix_dfs
├ generate_matrix_prim
├ generate_matrix_kruskal
├ generate_matrix_split
├ find_path_dfs
└ find_path_bfs (TODO) - 并查集类 UnionSet:
├ find
└ union - 可视化:
├ draw_cell
├ draw_path
├ draw_maze
├ check_reach
├ _eventHandler
├ _paint
├ _reset
└ update_maze
迷宫算法源码 mazeGenerator.py:
import numpy as np
import time
import random
import copy
class UnionSet(object):
"""
并查集实现,构造函数中的matrix是一个numpy类型
"""
def __init__(self, arr):
self.parent = {pos: pos for pos in arr}
self.count = len(arr)
def find(self, root):
if root == self.parent[root]:
return root
return self.find(self.parent[root])
def union(self, root1, root2):
self.parent[self.find(root1)] = self.find(root2)
class Maze(object):
"""
迷宫生成类
"""
def __init__(self, width = 11, height = 11):
assert width >= 5 and height >= 5, "Length of width or height must be larger than 5."
self.width = (width // 2) * 2 + 1
self.height = (height // 2) * 2 + 1
self.start = [1, 0]
self.destination = [self.height - 2, self.width - 1]
self.matrix = None
self.path = []
def print_matrix(self):
matrix = copy.deepcopy(self.matrix)
for p in self.path:
matrix[p[0]][p[1]] = 1
for i in range(self.height):
for j in range(self.width):
if matrix[i][j] == -1:
print('□', end = '')
elif matrix[i][j] == 0:
print(' ', end = '')
elif matrix[i][j] == 1:
print('■', end = '')
print('')
def generate_matrix_dfs(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.ones((self.height, self.width))
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
visit_flag = [[0 for i in range(self.width)] for j in range(self.height)]
def check(row, col, row_, col_):
temp_sum = 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
temp_sum += self.matrix[row_ + d[0]][col_ + d[1]]
return temp_sum <= -3
def dfs(row, col):
visit_flag[row][col] = 1
self.matrix[row][col] = 0
if row == self.start[0] and col == self.start[1] + 1:
return
directions = [[0, 2], [0, -2], [2, 0], [-2, 0]]
random.shuffle(directions)
for d in directions:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width - 1 and visit_flag[row_][col_] == 0 and check(row, col, row_, col_):
if row == row_:
visit_flag[row][min(col, col_) + 1] = 1
self.matrix[row][min(col, col_) + 1] = 0
else:
visit_flag[min(row, row_) + 1][col] = 1
self.matrix[min(row, row_) + 1][col] = 0
dfs(row_, col_)
dfs(self.destination[0], self.destination[1] - 1)
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1] + 1] = 0
# 虽然说是prim算法,但是我感觉更像随机广度优先算法
def generate_matrix_prim(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.ones((self.height, self.width))
def check(row, col):
temp_sum = 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
temp_sum += self.matrix[row + d[0]][col + d[1]]
return temp_sum < -3
queue = []
row, col = (np.random.randint(1, self.height - 1) // 2) * 2 + 1, (np.random.randint(1, self.width - 1) // 2) * 2 + 1
queue.append((row, col, -1, -1))
while len(queue) != 0:
row, col, r_, c_ = queue.pop(np.random.randint(0, len(queue)))
if check(row, col):
self.matrix[row, col] = 0
if r_ != -1 and row == r_:
self.matrix[row][min(col, c_) + 1] = 0
elif r_ != -1 and col == c_:
self.matrix[min(row, r_) + 1][col] = 0
for d in [[0, 2], [0, -2], [2, 0], [-2, 0]]:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width - 1 and self.matrix[row_][col_] == -1:
queue.append((row_, col_, row, col))
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
# 递归切分算法,还有问题,现在不可用
def generate_matrix_split(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.zeros((self.height, self.width))
self.matrix[0, :] = -1
self.matrix[self.height - 1, :] = -1
self.matrix[:, 0] = -1
self.matrix[:, self.width - 1] = -1
# 随机生成位于(start, end)之间的偶数
def get_random(start, end):
rand = np.random.randint(start, end)
if rand & 0x1 == 0:
return rand
return get_random(start, end)
# split函数的四个参数分别是左上角的行数、列数,右下角的行数、列数,墙壁只能在偶数行,偶数列
def split(lr, lc, rr, rc):
if rr - lr < 2 or rc - lc < 2:
return
# 生成墙壁,墙壁只能是偶数点
cur_row, cur_col = get_random(lr, rr), get_random(lc, rc)
for i in range(lc, rc + 1):
self.matrix[cur_row][i] = -1
for i in range(lr, rr + 1):
self.matrix[i][cur_col] = -1
# 挖穿三面墙得到连通图,挖孔的点只能是偶数点
wall_list = [
("left", cur_row, [lc + 1, cur_col - 1]),
("right", cur_row, [cur_col + 1, rc - 1]),
("top", cur_col, [lr + 1, cur_row - 1]),
("down", cur_col, [cur_row + 1, rr - 1])
]
random.shuffle(wall_list)
for wall in wall_list[:-1]:
if wall[2][1] - wall[2][0] < 1:
continue
if wall[0] in ["left", "right"]:
self.matrix[wall[1], get_random(wall[2][0], wall[2][1] + 1) + 1] = 0
else:
self.matrix[get_random(wall[2][0], wall[2][1] + 1), wall[1] + 1] = 0
# self.print_matrix()
# time.sleep(1)
# 递归
split(lr + 2, lc + 2, cur_row - 2, cur_col - 2)
split(lr + 2, cur_col + 2, cur_row - 2, rc - 2)
split(cur_row + 2, lc + 2, rr - 2, cur_col - 2)
split(cur_row + 2, cur_col + 2, rr - 2, rc - 2)
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
split(0, 0, self.height - 1, self.width - 1)
# 最小生成树算法-kruskal(选边法)思想生成迷宫地图,这种实现方法最复杂。
def generate_matrix_kruskal(self):
# 地图初始化,并将出口和入口处的值设置为0
self.matrix = -np.ones((self.height, self.width))
def check(row, col):
ans, counter = [], 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width - 1 and self.matrix[row_, col_] == -1:
ans.append([d[0] * 2, d[1] * 2])
counter += 1
if counter <= 1:
return []
return ans
nodes = set()
row = 1
while row < self.height:
col = 1
while col < self.width:
self.matrix[row, col] = 0
nodes.add((row, col))
col += 2
row += 2
unionset = UnionSet(nodes)
while unionset.count > 1:
row, col = nodes.pop()
directions = check(row, col)
if len(directions):
random.shuffle(directions)
for d in directions:
row_, col_ = row + d[0], col + d[1]
if unionset.find((row, col)) == unionset.find((row_, col_)):
continue
nodes.add((row, col))
unionset.count -= 1
unionset.union((row, col), (row_, col_))
if row == row_:
self.matrix[row][min(col, col_) + 1] = 0
else:
self.matrix[min(row, row_) + 1][col] = 0
break
self.matrix[self.start[0], self.start[1]] = 0
self.matrix[self.destination[0], self.destination[1]] = 0
# 迷宫寻路算法dfs
def find_path_dfs(self, destination):
visited = [[0 for i in range(self.width)] for j in range(self.height)]
def dfs(path):
visited[path[-1][0]][path[-1][1]] = 1
if path[-1][0] == destination[0] and path[-1][1] == destination[1]:
self.path = path[:]
return
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
row_, col_ = path[-1][0] + d[0], path[-1][1] + d[1]
if row_ > 0 and row_ < self.height - 1 and col_ > 0 and col_ < self.width and visited[row_][col_] == 0 and self.matrix[row_][col_] == 0:
dfs(path + [[row_, col_]])
dfs([[self.start[0], self.start[1]]])
if __name__ == '__main__':
maze = Maze(51, 51)
maze.generate_matrix_kruskal()
maze.print_matrix()
maze.find_path_dfs(maze.destination)
print("answer", maze.path)
maze.print_matrix()
- 1
迷宫可视化源码 maze.py:
import tkinter as tk
from mazeGenerator import Maze
import time
import copy
import numpy as np
import math
import threading
def draw_cell(canvas, row, col, color="#F2F2F2"):
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width, y0 + cell_width
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline =color, width = 0)
def draw_path(canvas, matrix, row, col, color, line_color):
# 列
if row + 1 < rows and matrix[row - 1][col] >= 1 and matrix[row + 1][col] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width
# 行
elif col + 1 < cols and matrix[row][col - 1] >= 1 and matrix[row][col + 1] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width, y0 + cell_width / 5
# 左上角
elif col + 1 < cols and row + 1 < rows and matrix[row][col + 1] >= 1 and matrix[row + 1][col] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
# 右上角
elif row + 1 < rows and matrix[row][col - 1] >= 1 and matrix[row + 1][col] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
# 左下角
elif col + 1 < cols and matrix[row - 1][col] >= 1 and matrix[row][col + 1] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
# 右下角
elif matrix[row - 1][col] >= 1 and matrix[row][col - 1] >= 1:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + 3 * cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + 3 * cell_width / 5
else:
x0, y0 = col * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5, row * cell_width + 2 * cell_width / 5
x1, y1 = x0 + cell_width / 5, y0 + cell_width / 5
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = color, outline = line_color, width = 0)
def draw_maze(canvas, matrix, path, moves):
"""
根据matrix中每个位置的值绘图:
-1: 墙壁
0: 空白
1: 参考路径
2: 移动过的位置
"""
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if matrix[r][c] == 0:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c)
elif matrix[r][c] == -1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, '#525288')
elif matrix[r][c] == 1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c)
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#bc84a8', '#bc84a8')
elif matrix[r][c] == 2:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c)
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#ee3f4d', '#ee3f4d')
for p in path:
matrix[p[0]][p[1]] = 1
for move in moves:
matrix[move[0]][move[1]] = 2
def update_maze(canvas, matrix, path, moves):
canvas.delete("all")
matrix = copy.copy(matrix)
for p in path:
matrix[p[0]][p[1]] = 1
for move in moves:
matrix[move[0]][move[1]] = 2
row, col = movement_list[-1]
colors = ['#525288', '#F2F2F2', '#525288', '#F2F2F2', '#525288', '#F2F2F2', '#525288', '#F2F2F2']
if level > 2:
colors = ['#232323', '#252525', '#2a2a32', '#424242', '#434368', '#b4b4b4', '#525288', '#F2F2F2']
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
distance = (row - r) * (row - r) + (col - c) * (col - c)
if distance >= 100:
color = colors[0:2]
elif distance >= 60:
color = colors[2:4]
elif distance >= 30:
color = colors[4:6]
else:
color = colors[6:8]
if matrix[r][c] == 0:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[1])
elif matrix[r][c] == -1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[0])
elif matrix[r][c] == 1:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[1])
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#bc84a8', '#bc84a8')
elif matrix[r][c] == 2:
draw_cell(canvas, r, c, color[1])
draw_path(canvas, matrix, r, c, '#ee3f4d', '#ee3f4d')
def check_reach():
global next_maze_flag
if movement_list[-1] == maze.destination:
print("Congratulations! You reach the goal! The step used: {}".format(click_counter))
x0, y0 = width / 2 - 200, 30
x1, y1 = x0 + 400, y0 + 40
canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = '#F2F2F2', outline ='#525288', width = 3)
canvas.create_text(width / 2, y0 + 20, text = "Congratulations! You reach the goal! Steps used: {}".format(click_counter), fill = "#525288")
next_maze_flag = True
def _eventHandler(event):
global movement_list
global click_counter
global next_maze_flag
global level
if not next_maze_flag and event.keysym in ['Left', 'Right', 'Up', 'Down']:
click_counter += 1
windows.title("Maze Level-{} Steps-{}".format(level, click_counter))
cur_pos = movement_list[-1]
ops = {'Left': [0, -1], 'Right': [0, 1], 'Up': [-1, 0], 'Down': [1, 0]}
r_, c_ = cur_pos[0] + ops[event.keysym][0], cur_pos[1] + ops[event.keysym][1]
if len(movement_list) > 1 and [r_, c_] == movement_list[-2]:
movement_list.pop()
while True:
cur_pos = movement_list[-1]
counter = 0
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
r_, c_ = cur_pos[0] + d[0], cur_pos[1] + d[1]
if c_ >= 0 and maze.matrix[r_][c_] == 0:
counter += 1
if counter != 2:
break
movement_list.pop()
elif r_ < maze.height and c_ < maze.width and maze.matrix[r_][c_] == 0:
while True:
movement_list.append([r_, c_])
temp_list = []
for d in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
r__, c__ = r_ + d[0], c_ + d[1]
if c__ < maze.width and maze.matrix[r__][c__] == 0 and [r__, c__] != cur_pos:
temp_list.append([r__, c__])
if len(temp_list) != 1:
break
cur_pos = [r_, c_]
r_, c_ = temp_list[0]
update_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
check_reach()
elif next_maze_flag:
next_maze_flag = False
movement_list = [maze.start]
click_counter = 0
maze.generate_matrix_kruskal()
maze.path = []
draw_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
level += 1
def _paint(event):
x, y = math.floor((event.y - 1) / cell_width), math.floor((event.x - 1) / cell_width)
if maze.matrix[x][y] == 0:
maze.find_path_dfs([x, y])
update_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
def _reset(event):
maze.path = []
update_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 基础参数
cell_width = 20
rows = 37
cols = 51
height = cell_width * rows
width = cell_width * cols
level = 1
click_counter = 0
next_maze_flag = False
windows = tk.Tk()
windows.title("Maze")
canvas = tk.Canvas(windows, background="#F2F2F2", width = width, height = height)
canvas.pack()
maze = Maze(cols, rows)
movement_list = [maze.start]
maze.generate_matrix_kruskal()
draw_maze(canvas, maze.matrix, maze.path, movement_list)
canvas.bind("<Button-1>", _paint)
canvas.bind("<Button-3>", _reset)
canvas.bind_all("<KeyPress>", _eventHandler)
windows.mainloop()
将以上两个代码分别保存到mazeGenerator.py 和maze.py,确保两个py文件在同一文件夹下,运行maze.py即可。
(暂时 完)
未经允许不得转载:萌萌guo angline - Apprentissage » python实现迷宫游戏实例源代码



 使用python批量爬取主流搜索引擎图片
使用python批量爬取主流搜索引擎图片 python爬虫关键词爬取百度的图片
python爬虫关键词爬取百度的图片 python库taichi太极人工智能tensoflow图形处理
python库taichi太极人工智能tensoflow图形处理 Selenium with Tor Browser using Python
Selenium with Tor Browser using Python shell.cloud.google保持在线
shell.cloud.google保持在线 run crontab with python selenium tor browser display in linux
run crontab with python selenium tor browser display in linux linux环境使用python调用tor浏览器随机浏览器网页
linux环境使用python调用tor浏览器随机浏览器网页
